BT
BT Porting and Usage Guide.
Overview
The K1 platform implements wireless communication through an external BT (Bluetooth) module (with UART/USB interfaces).
Functional Description
The Bluetooth architecture comprises the following layers:
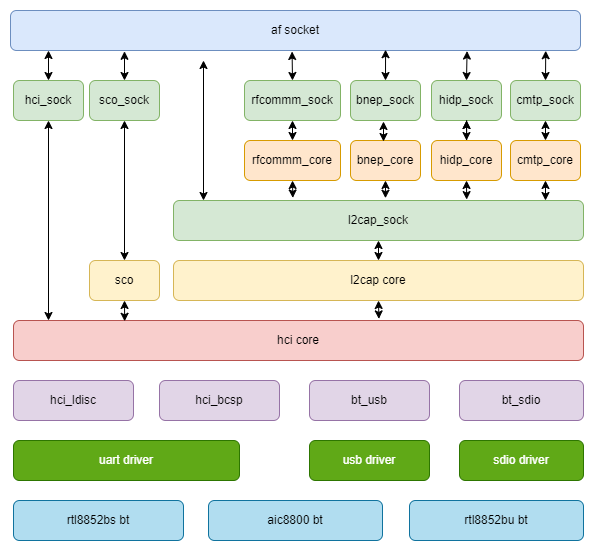
Source Code Structure
The BT-related source code can be divided into the following parts:
- Bluetooth Protocol Stack: Taking the BlueZ protocol stack as an example, the code is divided into two parts: kernel space and user space.
- BT HCI Driver: Primarily handles the HCI (Host Controller Interface) protocol layer implementation.
- Platform Support: Mainly implements module power supply and enable/disable control interfaces, which are called by the RFKILL driver.
- Interface Driver: Mainly implements the BT data transfer interface functions, such as UART, USB, etc.
BlueZ Protocol Stack Source Code is located in the following directories:
drivers/net/bluetooth
|-- af_bluetooth.c
|-- af_bluetooth.o
|-- bnep # Bluetooth network encapsulation protocol
│ |-- bnep.h
│ |-- core.c
│ |-- Kconfig
│ |-- Makefile
│ |-- netdev.c
│ |-- sock.c
|-- hci_codec.c
|-- hci_codec.h
|-- hci_conn.c
|-- hci_core.c # Hci core implementation
|-- hci_debugfs.c
|-- hci_debugfs.h
|-- hci_event.c
|-- hci_request.c
|-- hci_request.h
|-- hci_sock.c
|-- hci_sync.c
|-- hci_sysfs.c
|-- hidp # Bluetooth hid implementation
│ |-- core.c
│ |-- hidp.h
│ |-- Kconfig
│ |-- Makefile
│ |-- sock.c
|-- iso.c
|-- Kconfig
|-- l2cap_core.c # l2cap core implementation
|-- l2cap_sock.c
|-- lib.c
|-- Makefile
|-- mgmt.c # mgmt Bluetooth management implementation
|-- mgmt_config.c
|-- mgmt_config.h
|-- mgmt_util.c
|-- mgmt_util.h
|-- rfcomm # rfcomm protocol
│ |-- core.c
│ |-- Kconfig
│ |-- Makefile
│ |-- sock.c
│ |-- tty.c
|-- sco.c
|-- selftest.c
|-- selftest.h
|-- smp.c
|-- smp.h
HCI driver source code is located in the following directory::
drivers/bluetooth
|-- btbcm.c # Broadcom vendor implementation
|-- btrtl.c # Realtek vendor implementation
|-- btusb.c # hci UART implementation
|-- hci_h4.c # hci h4 implementation
|-- hci_h5.c # hci h5 implementation
|-- hci_ldisc.c # Bluetooth hci line discipline
Platform-specific source code:
drivers/soc/spacemit/spacemit-rf
|-- spacemit-pwrseq.c # Implementation for common parts of WIFI and Bluetooth
|-- spacemit-wlan.c # WIFI power supply, GPIO, and clock-related interface implementation
|-- spacemit-bt.c # BT power supply, GPIO, and clock-related interface implementation
Interface-related source code: Refer to the documentation for each interface driver.
Key Features
Platform UART Interface Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| 4-wire flow control support | Supports up to 3.6Mbps |
| DMA support | Supports DMA transfer mode |
Module Performance Specifications
| Module Mode | Specifications |
|---|---|
| rtl8852bs | Supports Bluetooth 5.2 |
| Supports Bluetooth 2.0 UART HCI H4/H5 | |
| aic8800d80 | Supports Bluetooth 5.3 |
| Supports Bluetooth 2.0 UART HCI H4 |
Configuration
It mainly includes driver enablement configuration and DTS configuration.
CONFIG Configuration
Protocol Stack Configuration
Networking support (NET [=y])
Bluetooth subsystem support (BT [=y])
Bluetooth Classic (BR/EDR) features (BT_BREDR [=y])
RFCOMM protocol support (BT_RFCOMM [=y])
RFCOMM TTY support (BT_RFCOMM_TTY [=y])
BNEP protocol support (BT_BNEP [=y])
HIDP protocol support (BT_HIDP [=y])
Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) features (BT_LE [=y])
Export Bluetooth internals in debugfs (BT_DEBUGFS [=y])
UART HCI Configuration
Networking support (NET [=y])
Bluetooth subsystem support (BT [=y])
Bluetooth device drivers
HCI UART driver (BT_HCIUART [=y])
UART (H4) protocol support (BT_HCIUART_H4 [=y])
Three-wire UART (H5) protocol support (BT_HCIUART_3WIRE [=y])
Realtek protocol support (BT_HCIUART_RTL [=y])
By default, H4 and H5 are supported, where the Realtek BT serial port uses the H5 protocol.
USB HCI Configuration
Networking support (NET [=y])
Bluetooth subsystem support (BT [=y])
Bluetooth device drivers
HCI USB driver (BT_HCIBTUSB [=m])
Broadcom protocol support (BT_HCIBTUSB_BCM [=y])
Realtek protocol support (BT_HCIBTUSB_RTL [=y])
BT_HCIBTUSB_BCM and BT_HCIBTUSB_RTL correspond to support for Broadcom and Realtek, respectively.
AVRCP Configuration
Device Drivers
Input device support
Generic input layer (needed for keyboard, mouse, ...) (INPUT [=y])
Miscellaneous devices (INPUT_MISC [=y])
User level driver support (INPUT_UINPUT [=y])
To deliver AVRCP key values and related information to user-space applications via the input device, the INPUT_UINPUT option must be enabled.
HOGP Configuration
Device Drivers
HID bus support (HID_SUPPORT [=y])
HID bus core support (HID[=y])
User-space I/O driver support for HID subsystem (UHID [=y])
To deliver HoGP key values (e.g., KEY_1, KEY_2, KEY_ESC) to user-space applications via the input device, the UHID option must be enabled.
Platform RFKILL Configuration
Device Drivers
SOC (System On Chip) specific Drivers
Spacemit rfkill driver (SPACEMIT_RFKILL [=y])
CONFIG_SPACEMIT_RFKILL provides platform-specific support for the BT module. By default, this option is set to Y.
DTS Configuration
UART Configuration
Typically, uart2 is used to connect to the Bluetooth module, with the device node being /dev/ttyS1:
&uart2 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_uart2>;
status = "okay";
};
UART2 pinctrl Configuration
The Bluetooth pin control configuration should be based on the actual hardware, and flow control is enabled by default.
pinctrl_uart2: uart2_grp {
pinctrl-single,pins =<
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_21, MUX_MODE1, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS2)) /* uart2_txd */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_22, MUX_MODE1, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS2)) /* uart2_rxd */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_23, MUX_MODE1, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS2)) /* uart2_cts_n */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_24, MUX_MODE1, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS2)) /* uart2_rts_n */
>;
};
Platform DTS Configuration
The complete platform solution configuration is as follows:
rf_pwrseq: rf-pwrseq {
compatible = "spacemit,rf-pwrseq";
//vdd-supply = <&ldo_7>;
//vdd_voltage = <3300000>;
io-supply = <&dcdc_3>;
io_voltage = <1800000>;
pwr-gpios = <&gpio 67 0>;
status = "okay";
wlan_pwrseq: wlan-pwrseq {
compatible = "spacemit,wlan-pwrseq";
regon-gpios = <&gpio 116 0>;
interrupt-parent = <&pinctrl>;
interrupts = <268>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_wlan_wakeup>;
};
bt_pwrseq: bt-pwrseq {
compatible = "spacemit,bt-pwrseq";
reset-gpios = <&gpio 63 0>;
};
};
-
rf_pwrseq:
vdd-supplyis the power supply configuration for the module, which should be set according to the actual hardware.vdd_voltageis used to set the voltage for the module's power supply.io-supplyis the power supply configuration for the module's IO, which should be set according to the actual hardware.io_voltageis used to set the voltage for the module's IO power supply.pwr-gpioss is the enable pin for the module. After configuration, it will be pulled high by default and supports the configuration of multiple GPIOs.clockis the clock configuration shared by the module.power-on-delay-msis the delay after the module is powered on, with a default value of 100ms.
-
bt_pwrseq:
reset-gpiosis the enable pin for Bluetooth. When enabling the corresponding RFKILL for Bluetooth, this GPIO will be pulled high.clockis the clock configuration for Bluetooth.power-on-delay-msis the delay after Bluetooth is powered on, with a default value of 10ms.
Many modules on the market are dual-purpose Wi-Fi and Bluetooth modules, and the power supply for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth is often shared. For this situation, it is recommended to configure the DTS as follows:
- Shared parts (affecting both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth) should be configured in
rf_pwrseq. - Parts that only affect Bluetooth should be configured in
bt_pwrseq.
For Bluetooth-only modules, only bt_pwrseq needs to be configured, and rf_pwrseq does not need to be configured. However, the rf_pwrseq node must still be enabled.
Power Control Logic Explanation
- When turning on Bluetooth power:
- The system will first enable the shared power supply (i.e.,
rf_pwrseq) and related GPIO states. - The platform will maintain a reference count internally.
- The system will first enable the shared power supply (i.e.,
- When turning off Bluetooth power: The shared power supply and GPIO states will only be truly turned off when both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are turned off.
Interface
UART hciattach
hciattach is an initialization tool provided by BlueZ for UART interface Bluetooth controllers. For Bluetooth devices with a USB interface, this part can be ignored.
-
Realtek Bluetooth UART Enter the
rtk_hciattach/directory, generate the executable filertk_hciattach, and then run:rtk_hciattach -n -s 115200 ttyS1 rtk_h5 & -
AIC8800 Bluetooth UART Initialize using
hciattachas follows:hciattach -s 1500000 /dev/ttyS1 any 1500000 flow nosleep
API
The platform encapsulates Bluetooth power on/off within the RFKILL subsystem, allowing direct control of Bluetooth power through RFKILL.
# rfkill list
0: spacemit-bt: Bluetooth
Soft blocked: no
Hard blocked: no
1: phy0: Wireless LAN
Soft blocked: no
Hard blocked: no
2: hci0: Bluetooth
Soft blocked: no
Hard blocked: no
# rfkill block blutooth
# rfkill list
0: spacemit-bt: Bluetooth
Soft blocked: yes
Hard blocked: no
1: phy0: Wireless LAN
Soft blocked: no
Hard blocked: no
2: hci0: Bluetooth
Soft blocked: yes
Hard blocked: no
Among them:
spacemit-btis the RFKILL Bluetooth device registered by the platform.hci0is the RFKILL device registered by the Bluetooth Protocol Stack.
During platform initialization, you only need to actively turn on the Bluetooth device corresponding to spacemit-bt:
cat /sys/class/rfkill/rfkill0/type
bluetooth
cat /sys/class/rfkill/rfkill0/name
spacemit-bt
echo 1 > /sys/class/rfkill/rfkill0/state
When operating RFKILL, you need to confirm that the type and name correspond to the Bluetooth device of spacemit-bt.
Debugging
sysfs
You can query the status information of rfkill under sysfs:
cat /sys/class/rfkill/rfkill0/state
1
sysfs can also be used to query information about the corresponding UART.
/sys/devices/platform/soc/d4017100.uart
debugfs
You can query information related to Bluetooth stack components under debugfs:
/sys/kernel/debug/bluetooth# ls
hci0 l2cap rfcomm rfcomm_dlc sco
Testing
Interact with the bluetoothctl service using bluetoothd.
First, ensure that the bluetoothd service is running properly, and then enter the following command to access the command line:
[bluetooth]# power on
[bluetooth]# Changing power on succeeded
[bluetooth]# scan on
[bluetooth]# SetDiscoveryFilter success
[bluetooth]# Discovery started
[bluetooth]# [CHG] Controller 5C:8A:AE:67:62:04 Discovering: yes
[bluetooth]# [NEW] Device 45:DC:1E:BC:2C:77 45-DC-1E-BC-2C-77
[bluetooth]# [NEW] Device 4C:30:B8:02:7F:7A 4C-30-B8-02-7F-7A
[bluetooth]# [NEW] Device DC:28:67:9A:70:8E DC-28-67-9A-70-8E
[bluetooth]# [NEW] Device 58:FB:F1:17:D4:19 58-FB-F1-17-D4-19
[bluetooth]# [NEW] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D 84-7B-57-FB-20-8D
[bluetooth]# [CHG] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D TxPower: 0x000c (12)
[bluetooth]# [CHG] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D Name: LT-ZHENGHONG
[bluetooth]# [CHG] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D Alias: LT-ZHENGHONG
[bluetooth]# [CHG] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D UUIDs: 0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[bluetooth]# [CHG] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D UUIDs: 0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[bluetooth]# [CHG] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D UUIDs: 0000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[bluetooth]# [CHG] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D UUIDs: 0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[bluetooth]# [CHG] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D UUIDs: 0000111f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[bluetooth]# [CHG] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D UUIDs: 0000111e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb
[bluetooth]#
[bluetooth]# pair 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D
Attempting to pair with 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D
[CHG] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D Connected: yes
[LT-ZHENGHONG]# Request confirmation
[LT-ZHENGHONG]# 1;39m[agent] Confirm passkey 947781 (yes/no): yes
[DEL] Device 58:FB:F1:17:D4:19 58-FB-F1-17-D4-19
[bluetooth]# info 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D
Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D (public)
Name: LT-ZHENGHONG
Alias: LT-ZHENGHONG
Class: 0x002a010c (2752780)
Icon: computer
Paired: no
Bonded: no
Trusted: no
Blocked: no
Connected: yes
LegacyPairing: no
UUID: A/V Remote Control Target (0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Audio Source (0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: A/V Remote Control (0000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Audio Sink (0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Handsfree Audio Gateway (0000111f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Handsfree (0000111e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
RSSI: 0xffffffae (-82)
TxPower: 0x000c (12)
[LT-ZHENGHONG]# [DEL] Device DC:28:67:9A:70:8E DC-28-67-9A-70-8E
[LT-ZHENGHONG]# [DEL] Device 45:DC:1E:BC:2C:77 45-DC-1E-BC-2C-77
[LT-ZHENGHONG]# [DEL] Device 53:84:3E:02:79:84 53-84-3E-02-79-84
[LT-ZHENGHONG]# [CHG] Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D Bonded: yes
[LT-ZHENGHONG]# info 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D
Device 84:7B:57:FB:20:8D (public)
Name: LT-ZHENGHONG
Alias: LT-ZHENGHONG
Class: 0x002a010c (2752780)
Icon: computer
Paired: no
Bonded: yes
Trusted: no
Blocked: no
Connected: yes
LegacyPairing: no
UUID: A/V Remote Control Target (0000110c-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Audio Source (0000110a-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: A/V Remote Control (0000110e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Audio Sink (0000110b-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Handsfree Audio Gateway (0000111f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
UUID: Handsfree (0000111e-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb)
RSSI: 0xffffffae (-82)
TxPower: 0x000c (12)
FAQ
Question 1: Bluetooth Initialization Failure
Symptom: hciattach initialization fails.
Log Output::
Realtek Bluetooth :Realtek Bluetooth init UART with init speed:115200, type:HCI UART H5
Realtek Bluetooth :Realtek hciattach version 3.1.4796cb2.20230921-183414
Realtek Bluetooth :Use epoll
Realtek Bluetooth WARN: Writev partially, ret 0
Realtek Bluetooth WARN: OP_H5_SYNC Transmission timeout
Realtek Bluetooth WARN: Writev partial, 0
Realtek Bluetooth WARN: OP_H5_SYNC Transmission timeout
Realtek Bluetooth WARN: Writev partial, 0
Realtek Bluetooth WARN: OP_H5_SYNC Transmission timeout
Realtek Bluetooth WARN: Writev partial, 0
Solution:
- Verify that the power supply for the Bluetooth module is functioning correctly.