PWM
PWM Functionality and Usage Guide.
Overview
The PWM controller is an electronic component that adjusts output signals by modulating pulse widths.
Function Overview
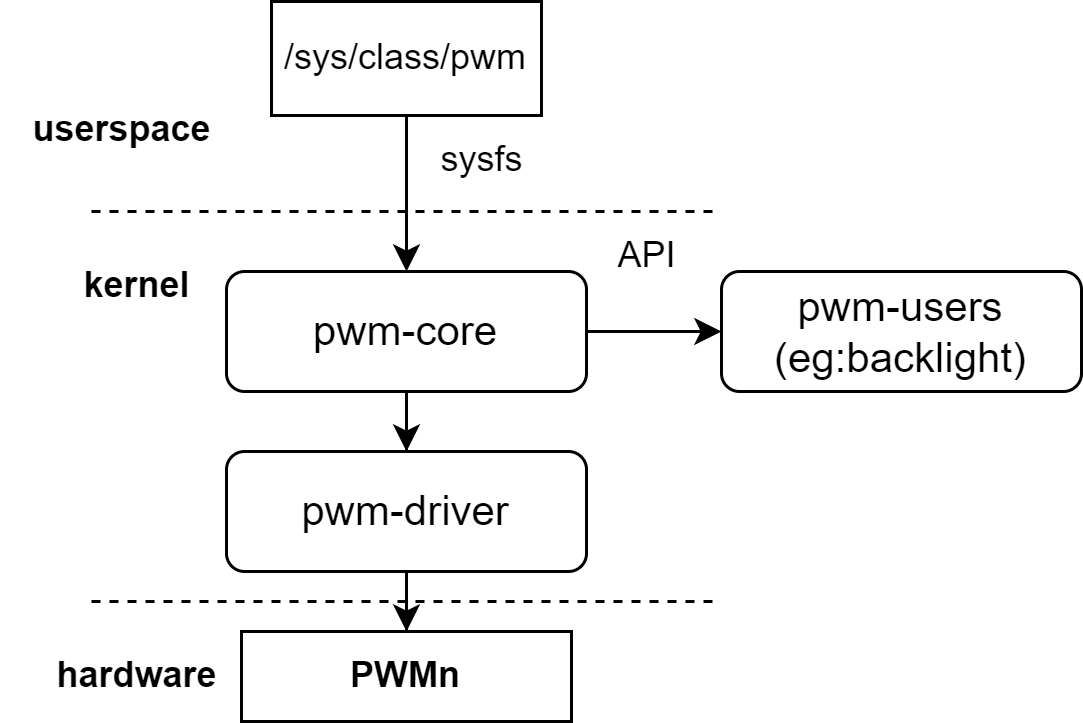
The kernel’s PWM framework enables modules to request PWM controllers and manage signal output.
For example, fan speed control and backlight brightness in the kernel can both be controlled using PWM.
Source Code Structure
The PWM controller driver code is located in the drivers/pwm directory:
drivers/pwm
|--core.c # Kernel PWM framework interface code
|--pwm-sysfs.c # Code for registering the PWM framework to sysfs
|--pwm-pxa.c # K1 PWM driver
Key Features
- Capable of generating PWM signals from 200Hz to 6.4MHz
- The K1 platform supports 20 configurable PWM channels
Configuration
It mainly includes driver enablement configuration and DTS configuration.
CONFIG Configuration
CONFIG_PWM
This provides support for the kernel platform PWM framework. When supporting the K1 PWM driver, it should be set to Y.
Symbol: PWM [=y]
Device Drivers
-> Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) Support (PWM [=y])
After enabling the platform layer PWM framework, set CONFIG_PWM_PXA to Y to support the K1 PWM driver.
Symbol: PWM_PXA [=y]
->PXA PWM support (PWM_PXA [=y])
DTS Configuration
Since the usage and configuration methods for the 20 PWM channels are similar, here we use PWM0 as an example.
pinctrl
You can refer to the PWM node configurations in the Linux repository at arch/riscv/boot/dts/spacemit/k1-x_pinctrl.dtsi. Here is an example:
pinctrl_pwm0_1: pwm0_1_grp {
pinctrl-single,pins =<
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_14, MUX_MODE3, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS2)) /* pwm0 */
>;
};
dtsi Configuration Example
In the dtsi, configure the base address of the PWM controller and the clock reset resources. Usually, these settings stay unchanged under normal circumstances.
1351 pwm0: pwm@d401a000 {
1352 compatible = "spacemit,k1x-pwm";
1353 reg = <0x0 0xd401a000 0x0 0x10>;
1354 #pwm-cells = <1>;
1355 clocks = <&ccu CLK_PWM0>;
1356 resets = <&reset RESET_PWM0>;
1357 k1x,pwm-disable-fd;
1358 status = "disabled";
1359 };
DTS Configuration Example
The complete DTS configuration is shown below.
807 &pwm0 {
808 pinctrl-names = "default";
809 pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_pwm0_1>;
810 status = "okay";
811 };
Interface
API
The Linux kernel implements references and adjustments to PWM for other devices or frameworks such as backlight, LEDs, and fans. Commonly used APIs include:
struct pwm_device *devm_pwm_get(struct device *dev, const char *con_id)
# This interface retrieves a PWM resource from the PWM framework
int pwm_apply_state(struct pwm_device *pwm, const struct pwm_state *state)
# This interface sets the state of the PWM.
Debugging
PWM can be configured via sysfs without programming, using shell commands. You can test it by connecting a speed-adjustable fan to the corresponding PWM pin. The process is as follows. This is verified on the Buildroot system.
# cd /sys/class/pwm/
# ls # Each node represents an LED light
pwmchip0 pwmchip1 pwmchip2 pwmchip3 pwmchip4 pwmchip5 pwmchip6
# echo 0 > pwmchip0/export
# ls pwmchip0/pwm0/
capture enable polarity uevent
duty_cycle period power
# Set the time for one period of the PWM signal, in nanoseconds. For example, to set the frequency to 1kHz, the period would be 1,000,000 ns (1 second / 1000 Hz)
# echo 1000000 > pwmchip0/pwm0/period
# Set the duty cycle of the PWM signal.
# echo 500000 > pwmchip0/pwm0/duty_cycle
# Enable the PWM signal.
# echo 1 > pwmchip0/pwm0/enable
# Adjust the duty cycle, which will reduce the fan speed
# echo 50000 > pwmchip0/pwm0/duty_cycle
# Disable the PWM signal.
# echo 0 > pwmchip0/pwm0/enable
Note: The available pwmchipx in sysfs are PWMs that have not been used. If a PWM has already been requested by a kernel driver through an interface like
pwm_get, then that PWM cannot be configured through sysfs.
Testing
The high/low level of the PWM output signal can be adjusted by controlling the duty cycle. For practical testing, you can use the PWM nodes in sysfs and a speed-adjustable PWM fan