Audio
Audio Functionality and Usage Guide.
Overview
The Audio module includes 2 I2S interfaces and 1 HDMI audio interface.
Functional Description
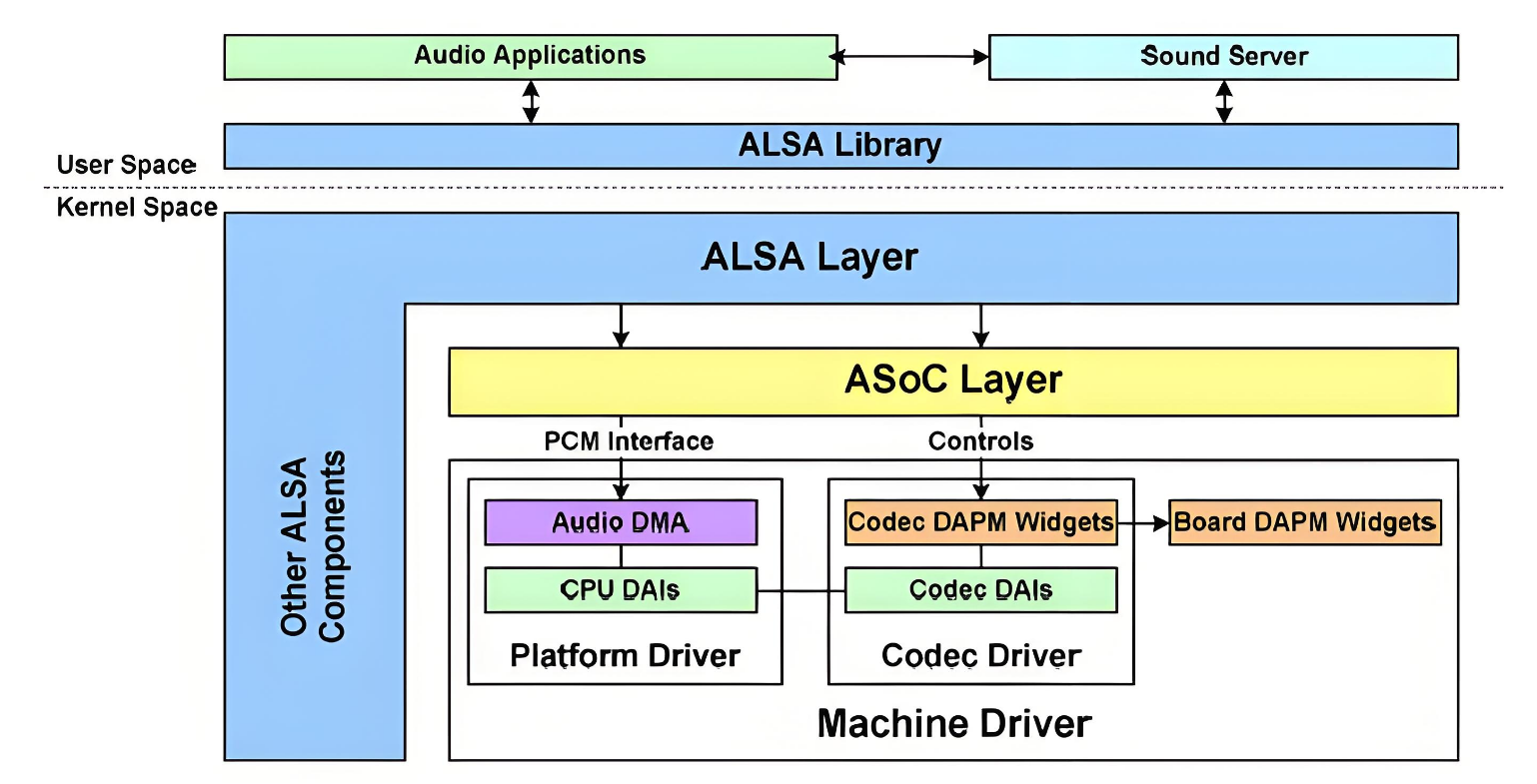
The ALSA audio framework can be divided into several layers:
-
ALSA Library
Provides a unified API interface to applications. Various applications can achieve playback, recording, and control by calling the APIs provided by the ALSA library. Two basic libraries are currently provided: tinyalsa, which is a simplified version of the ALSA library, is mainly used in Android systems.
-
ALSA CORE
The core layer of ALSA, which provides logical devices (PCM, CTL, MIDI, TIMER, etc.) for system calls and drives hardware devices (Machine, I2S, DMA, CODEC).
-
ASoC Core
The standard framework of ALSA, which is the core part of the ALSA-driver. It provides general methods and data structures for various audio device drivers.
-
Hardware Driver
The audio hardware device driver, which consists of three main parts: Machine, Platform, and Codec. It provides the ALSA Driver API and the initialization and workflow of the corresponding audio devices, implementing specific functional components. This is the part that driver developers need to implement specifically.
-
Machine
Typically refers to a specific single board that includes particular peripherals, providing a carrier for the CPU and Codec. Machine drivers are almost non-reusable. The Machine driver links the Platform driver and the Codec driver together, specifying which Platform driver to use, which SoC-side DAI (Digital Audio Interface) to use, which Codec driver to use, and which DAI interface on the Codec to use, while also performing operations specific to the single board.
-
Platform
Generally refers to a specific SoC platform, which can be understood as a particular SoC with I2S, AC97 audio interfaces, internal clocks, and DMA units for audio data transfer. The Platform driver is only related to a specific SoC, implementing the SoC's audio DMA driver and the DAI interface driver on the SoC side. It is only related to the SoC and not to the Machine, allowing the Platform to be abstracted out so that the same SoC can be used in different Machines without any modifications.
-
Codec
The audio codec, which includes I2S interfaces, D/A, A/D, Mixer, and PA (Power Amplifier). It typically contains multiple inputs (Mic, Line-in, I2S, PCM) and several outputs (headphones, speakers, earpiece, Line-out). The SoC usually controls the codec chip via I2C. The Codec driver is only related to the Codec and is independent of the SoC and Machine. Like the Platform, the Codec should be implemented as a reusable component, allowing the same Codec to be used in different Machines.
Audio Solution
K1 currently supports two sound card solutions: Solution 1: HDMI Audio, which supports playback. Solution 2: I2S0 paired with an external I2C Codec ES8326B, which supports both playback and recording.
Source Code Structure
The I2S/HDMIAUDIO controller driver code is located in the sound/soc/spacemit directory:
sound/soc/spacemit
├── Kconfig
├── Makefile
├── spacemit-dummy-codec.c # Dummy codec, used with HDMI audio to create a sound card
├── spacemit-snd-card.c # Sound card driver
├── spacemit-snd-i2s.c # I2S driver
├── spacemit-snd-i2s.h
├── spacemit-snd-pcm-dma.c # Platform driver, mainly related to PCM
├── spacemit-snd-sspa.c # HDMI audio driver
├── spacemit-snd-sspa.h
The driver code for the Codec ES8326B is located in the sound/soc/codec directory:
sound/soc/codec
├── es8326.c
├── es8326.h
I2S
Key Features
- Supports a sampling rate of 48000, with a 16-bit sampling depth and 2 channels.
- Supports playback and recording functions.
- Supports full-duplex operation.
Configuration
The configuration mainly includes driver enabling and DTS (Device Tree Source) configuration
CONFIG Configuration
Audio Function Support
CONFIG_SOUND, CONFIG_SND, and CONFIG_SND_SOC provide support for the ALSA audio driver framework. By default, these options are enabled (y).
Device Drivers
Sound card support (SOUND [=y])
Advanced Linux Sound Architecture (SND [=y])
ALSA for SoC audio support (SND_SOC [=y])
Audio Function Support
CONFIG_SND_SOC_SPACEMIT, CONFIG_SPACEMIT_CARD, and CONFIG_SPACEMIT_PCM provide support for the K1 audio functionality. By default, these options are enabled (y)
Device Drivers
Sound card support (SOUND [=y])
Advanced Linux Sound Architecture (SND [=y])
ALSA for SoC audio support (SND_SOC [=y])
SoC Audio for SPACEMIT System-on-Chip (SND_SOC_SPACEMIT [=y])
Audio Simple Card (SPACEMIT_CARD [=y])
Audio Platform Pcm (SPACEMIT_PCM [=y])
I2S Function Support
CONFIG_SPACEMIT_I2S provides support for the I2S functionality. By default, this option is enabled (y).
Device Drivers
Sound card support (SOUND [=y])
Advanced Linux Sound Architecture (SND [=y])
ALSA for SoC audio support (SND_SOC [=y])
SoC Audio for SPACEMIT System-on-Chip (SND_SOC_SPACEMIT [=y])
Audio Simple Card (SPACEMIT_CARD [=y])
Audio Platform Pcm (SPACEMIT_PCM [=y])
Audio Cpudai I2S (SPACEMIT_I2S [=y])
DTS Configuration
pinctrl
- i2s0 pinctrl configuration There are two sets of pinctrl configurations, which should be configured according to the actual hardware design.
pinctrl_sspa0_0: sspa0_0_grp {
pinctrl-single,pins =<
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_118, MUX_MODE3, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa0_clk */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_119, MUX_MODE3, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa0_frm */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_120, MUX_MODE3, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa0_txd */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_121, MUX_MODE3, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa0_rxd */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_122, MUX_MODE3, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa0_sysclk */
>;
};
pinctrl_sspa0_1: sspa0_1_grp {
pinctrl-single,pins =<
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_58, MUX_MODE2, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa0_sysclk */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_111, MUX_MODE2, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa0_clk */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_112, MUX_MODE2, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa0_frm */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_113, MUX_MODE2, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa0_txd */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_114, MUX_MODE2, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa0_rxd */
>;
}
&i2s0 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_sspa0_0>; # Using the pin set pinctrl_sspa0_0.
status = "okay";
};
-
i2s1 pinctrl configuration
pinctrl_sspa1: sspa1_grp {
pinctrl-single,pins =<
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_24, MUX_MODE3, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa1_sysclk */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_25, MUX_MODE1, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa1_sclk */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_26, MUX_MODE1, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa1_frm */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_27, MUX_MODE1, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa1_txd */
K1X_PADCONF(GPIO_28, MUX_MODE1, (EDGE_NONE | PULL_UP | PAD_1V8_DS0)) /* sspa1_rxd */
>;
};
&i2s1 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_sspa1>; #Using the pin set pinctrl_sspa1.
status = "okay";
};
I2S-Codec Sound Card Configuration
Codec Configuration
Using the ES8326B Codec as an example for a complete sound card configuration.
Config Configuration
Enable the ES8326B configuration.
Device Drivers│
Sound card support (SOUND [=y])
Advanced Linux Sound Architecture (SND [=y])
ALSA for SoC audio support (SND_SOC [=y])
CODEC drivers
Everest Semi ES8326 CODEC (SND_SOC_ES8326 [=y])
DTS Configuration
-
GPIO Configure according to the actual hardware design. For example, on some K1 development boards, the ES8326B uses GPIO129 for headphone detection and GPIO127 for speaker control.
es8326: es8326@19{
interrupt-parent = <&gpio>;
interrupts = <126 1>; # Headphone insertion and removal detection
spk-ctl-gpio = <&gpio 127 0>; # Board-level speaker control GPIO
};
DTS Configuration Example
The complete configuration for the ES8236B codec is as follows:
es8326: es8326@19{
compatible = "everest,es8326";
reg = <0x19>;
#sound-dai-cells = <0>;
interrupt-parent = <&gpio>;
interrupts = <126 1>; # Headphone plug detection
spk-ctl-gpio = <&gpio 127 0>; # Board-level speaker control GPIO
everest,mic1-src = [44]; # ADC source configuration
everest,mic2-src = [66];
status = "okay";
};
MCLK Configuration
The ES8326B codec's MCLK is provided by I2S0 and is configured in the sound card node sound_codec
&sound_codec {
status = "okay";
simple-audio-card,name = "snd-es8326";
spacemit,mclk-fs = <64>; # Configure mclk = 64 * fs, i.e., 3.072MHz
simple-audio-card,codec {
simple-audio-card,codec {
sound-dai = <&es8326>;
};
};
};
Note. The spacemit,mclk-fs only supports configurations of 64, 128, or 256, which correspond to 3.072MHz, 6.144MHz, and 12.288MHz respectively.
Sound Card Configuration
DTS Configuration
sound_codec: snd-card@1 {
compatible = "spacemit,simple-audio-card";
simple-audio-card,format = "i2s";
status = "disabled";
interconnects = <&dram_range4>;
interconnect-names = "dma-mem";
spacemit,init-jack;
simple-audio-card,cpu { # CPU DAI Configuration
sound-dai = <&i2s0>;
};
simple-audio-card,plat {
sound-dai = <&i2s0_dma>; # Platform PCM Configuration
};
};
&sound_codec {
status = "okay";
simple-audio-card,name = "snd-es8326";
spacemit,mclk-fs = <64>;
simple-audio-card,codec {
sound-dai = <&es8326>; # Codec DAI Configuration
};
};
HDMIAUDIO
Key Features
- Supports a sample rate of 48,000 Hz, 16-bit sample depth, and 2 channels.
- Supports playback only
Configuration
The configuration mainly consists of driver enablement and DTS settings. Since HDMIAUDIO relies on the HDMI display function, it is necessary to ensure that HDMI display is supported. Please refer to the corresponding documentation.
CONFIG Configuration
Audio Function Support
CONFIG_SOUND, CONFIG_SND, and CONFIG_SND_SOC provide support for the ALSA audio driver framework. By default, this option is set to Y.
Device Drivers
Sound card support (SOUND [=y])
Advanced Linux Sound Architecture (SND [=y])
ALSA for SoC audio support (SND_SOC [=y])
K1 Audio Function Support
CONFIG_SND_SOC_SPACEMIT, CONFIG_SPACEMIT_CARD, and CONFIG_SPACEMIT_PCM provide support for K1 audio functions. By default, this option is set to Y.
Device Drivers
Sound card support (SOUND [=y])
Advanced Linux Sound Architecture (SND [=y])
ALSA for SoC audio support (SND_SOC [=y])
SoC Audio for SPACEMIT System-on-Chip (SND_SOC_SPACEMIT [=y])
Audio Simple Card (SPACEMIT_CARD [=y])
Audio Platform Pcm (SPACEMIT_PCM [=y])
HDMIAUDIO Function Support
CONFIG_SPACEMIT_HDMIAUDIO and CONFIG_SPACEMIT_DUMMYCODEC provide support for the HDMIAUDIO function. By default, this option is set to Y.
Device Drivers
Sound card support (SOUND [=y])
Advanced Linux Sound Architecture (SND [=y])
ALSA for SoC audio support (SND_SOC [=y])
SoC Audio for SPACEMIT System-on-Chip (SND_SOC_SPACEMIT [=y])
Audio Simple Card (SPACEMIT_CARD [=y])
Audio Platform Pcm (SPACEMIT_PCM [=y])
Audio Cpudai HDMI Audio (SPACEMIT_HDMIAUDIO [=y])
Audio CodecDai Dummy Codec (SPACEMIT_DUMMYCODEC [=y])
DTS Configuration
&hdmiaudio {
status = "okay";
};
HDMIAUDIO Sound Card Configuration
DTS Configuration
sound_hdmi: snd-card@0 {
compatible = "spacemit,simple-audio-card";
simple-audio-card,name = "snd-hdmi";
status = "disabled";
interconnects = <&dram_range4>;
interconnect-names = "dma-mem";
simple-audio-card,plat { # Platform PCM Configuration
sound-dai = <&hdmi_dma>;
};
simple-audio-card,codec { # Codec DAI Configuration
sound-dai = <&dummy_codec>;
};
};
&sound_hdmi {
status = "okay";
simple-audio-card,cpu {
sound-dai = <&hdmiaudio>; # CPU DAI Configuration
};
};
Interface
API
Please refer to the relevant official Linux documentation.
Debugging
You can perform debugging through the nodes under /proc/asound/.
View Sound Card Devices
root:/# cat /proc/asound/pcm
00-00: SSPA2-dummy_codec dummy_codec-0 : : playback 1
01-00: i2s-dai0-ES8326 HiFi ES8326 HiFi-0 : : playback 1 : capture 1
root:/#
Viewing Sound Card Status and Other Information
-
CLOSED, the sound card is in a closed state.
root:/# cat /proc/asound/card1/pcm0p/sub0/status
closed
root:/# cat /proc/asound/card1/pcm0p/sub0/hw_params
closed
root:/# -
RUNNING, the sound card is in a running state, either playing or recording. You can view the status and parameters of the sound card.
root:/# cat /proc/asound/card1/pcm0p/sub0/status
state: RUNNING
owner_pid : 3767
trigger_time: 224110.719883196
tstamp : 224164.735391138
delay : 2048
avail : 2048
avail_max : 2048
-----
hw_ptr : 2592768
appl_ptr : 2594816
root:/# cat /proc/asound/card1/pcm0p/sub0/status
state: RUNNING
owner_pid : 3767
trigger_time: 224110.719883196
tstamp : 224166.975406348
delay : 3072
avail : 1024
avail_max : 2048
-----
hw_ptr : 2700288
appl_ptr : 2703360
root:/# cat /proc/asound/card1/pcm0p/sub0/hw_params
access: RW_INTERLEAVED
format: S16_LE
subformat: STD
channels: 2
rate: 48000 (48000/1)
period_size: 1024
buffer_size: 4096
root:/#
Testing
Audio functionality can be tested using the alsa-utils or tinyalsa tools, which are already integrated into buildroot.
Playback Test
Viewing Playback Devices
aplay-l // List playback devices
root:/# aplay -l
**** PLAYBACK Hardware Devices ****
card 0: sndhdmi [snd-hdmi], device 0: SSPA2-dummy_codec dummy_codec-0 []
Subdevices: 1/1
Subdevice #0: subdevice #0
card 1: sndes8326 [snd-es8326], device 0: i2s-dai0-ES8326 HiFi ES8326 HiFi-0 []
Subdevices: 1/1
Subdevice #0: subdevice #0
root:/#
There are two playback devices visible:
- The HDMIAUDIO playback device has a card ID of 0 and a device ID of 0.
- The I2S-Codec playback device has a card ID of 1 and a device ID of 0.
Playback
Specify the card and device IDs to select a playback device
Example: Select the HDMIAUDIO sound card for playback.
aplay -Dhw:0,0 -r 48000 -f S16_LE --period-size=480 --buffer-size=1920 xxx.wav
Example: Select the I2S-Codec sound card for playback.
aplay -Dhw:1,0 -r 48000 -f S16_LE --period-size=1024 --buffer-size=4096 xxx.wav
Recording Test
Viewing Capture Devices
arecord -l to view the capture devices
root@spacemit-k1-x-deb1-board:~# arecord -l
**** CAPTURE Hardware Devices ****
card 1: sndes8326 [snd-es8326], device 0: i2s-dai0-ES8326 HiFi ES8326 HiFi-0 []
Subdevices: 1/1
Subdevice #0: subdevice #0
root@spacemit-k1-x-deb1-board:~#
There is one capture device visible:
- The I2S-Codec capture device has a card ID of 1 and a device ID of 0.
Recording
Select a device for recording by specifying the card ID and device ID.
Example: Select the I2S-Codec sound card for recording.
arecord -Dhw:1,0 -r 48000 -c 2 -f S16_LE --period-size=1024 --buffer-size=4096 xxx.wav