Thermal
Thermal Functionality and Usage Guide.
Overview
Thermal refers to a driver framework for temperature control mechanisms. The Linux Thermal framework is an architecture used in Linux systems for temperature control, primarily aimed at addressing the increasingly severe heat dissipation issues caused by the continuous enhancement of device performance.
Function Description
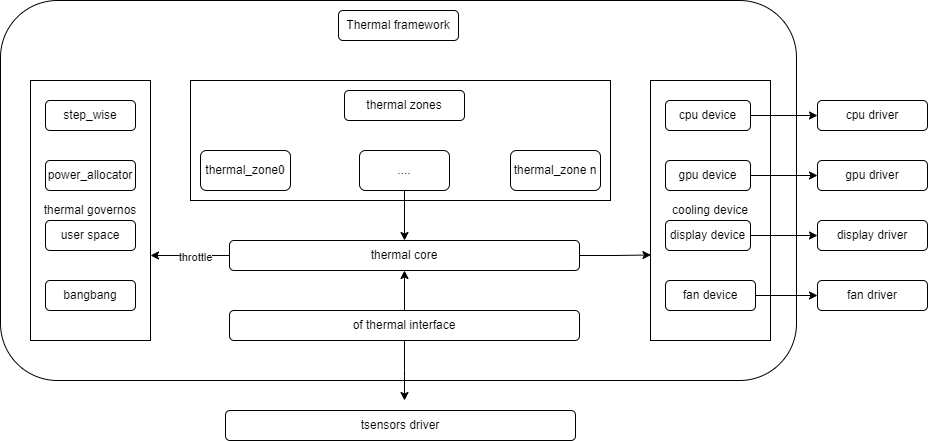
-
thermal_cooling_device
This corresponds to the driver that implements cooling measures and is the executor of thermal control.
-
thermal core
The core component of the thermal framework, responsible for driver initialization, managing interactions between
thermal_zone,governor, andcooling_device, and exposing user-space interfaces viasysfs. -
thermal governor
The temperature control algorithm, which determines which cooling state the cooling device should select when thermal control is triggered.
-
thermal zone device
Primarily used to create thermal zone nodes and connect thermal sensors. The nodes are located in the
/sys/class/thermaldirectory and are generated by the DTS (Device Tree Source) file configuration. -
thermal sensor
The temperature sensor, which mainly provides temperature data to the thermal framework.
Source Code Structure
The directory structure for the CPU frequency scaling platform driver is as follows:
drivers/thermal/
├── cpufreq_cooling.c
├── cpufreq_cooling.o
├── cpuidle_cooling.c
├── devfreq_cooling.c
├── gov_bang_bang.c
├── gov_fair_share.c
├── gov_power_allocator.c
├── gov_step_wise.c
├── gov_user_space.c
├── k1x-thermal.c ---> Platform driver
├── k1x-thermal.h
├── thermal_core.c
├── thermal_core.h
├── thermal_helpers.c
├── thermal_hwmon.c
├── thermal_hwmon.h
├── thermal_of.c
├── thermal_sysfs.c
Key Features
- Supports CPU temperature control.
- Triggers a system shutdown at 115°C to prevent overheating.
Testing Method
Use an external temperature probe or high-load application to induce temperature fluctuations. Check the thermal and cpufreq nodes to confirm whether the CPU temperature adjustment meets expectations.
-
Check the thermal sensor node:
cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone1/temp -
Check the CPU frequency scaling node:
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/policy0/scaling_cur_freq
Configuration Introduction
It mainly includes Driver Enable Configuration and DTS Configuration.
CONFIG Configuration
Thermal driver configuration is as follows:
CONFIG_K1X_THERMAL:
Enable this option if you want to have support for thermal management
controller present in Spacemit SoCs
Symbol: K1X_THERMAL [=y]
Type : tristate
Defined at drivers/thermal/Kconfig:450
Prompt: Spacemit K1X Thermal Support
Depends on: THERMAL [=y] && OF [=y] && SOC_SPACEMIT [=y]
Location:
-> Device Drivers
-> Thermal drivers (THERMAL [=y])
-> Spacemit K1X Thermal Support (K1X_THERMAL [=y])
DTS Configuration
&thermal_zones {
cluster0_thermal {
polling-delay = <0>;
polling-delay-passive = <0>;
thermal-sensors = <&thermal 3>;
thermal0_trips: trips {
cls0_trip0: cls0-trip-point0 {
temperature = <75000>;
hysteresis = <5000>;
type = "passive";
};
cls0_trip1: cls0-trip-point1 {
temperature = <85000>;
hysteresis = <5000>;
type = "passive";
};
cls0_trip2: cls0-trip-point2 {
temperature = <95000>;
hysteresis = <5000>;
type = "passive";
};
cls0_trip3: cls0-trip-point3 {
temperature = <105000>;
hysteresis = <5000>;
type = "passive";
};
cls0_trip4: cls0-trip-point4 {
temperature = <115000>;
hysteresis = <5000>;
type = "critical";
};
};
cooling-maps {
map0 {
trip = <&cls0_trip0>;
cooling-device = <&cpu_0 0 0>,
<&cpu_1 0 0>,
<&cpu_2 0 0>,
<&cpu_3 0 0>,
<&cpu_4 0 0>,
<&cpu_5 0 0>,
<&cpu_6 0 0>,
<&cpu_7 0 0>;
};
map1 {
trip = <&cls0_trip1>;
cooling-device = <&cpu_0 1 1>,
<&cpu_1 1 1>,
<&cpu_2 1 1>,
<&cpu_3 1 1>,
<&cpu_4 1 1>,
<&cpu_5 1 1>,
<&cpu_6 1 1>,
<&cpu_7 1 1>;
};
map2 {
trip = <&cls0_trip2>;
cooling-device = <&cpu_0 2 3>,
<&cpu_1 2 3>,
<&cpu_2 2 3>,
<&cpu_3 2 3>,
<&cpu_4 2 3>,
<&cpu_5 2 3>,
<&cpu_6 2 3>,
<&cpu_7 2 3>;
};
map3 {
trip = <&cls0_trip3>;
cooling-device = <&cpu_0 4 5>,
<&cpu_1 4 5>,
<&cpu_2 4 5>,
<&cpu_3 4 5>,
<&cpu_4 4 5>,
<&cpu_5 4 5>,
<&cpu_6 4 5>,
<&cpu_7 4 5>;
};
};
};
cluster1_thermal {
polling-delay = <0>;
polling-delay-passive = <0>;
thermal-sensors = <&thermal 4>;
thermal1_trips: trips {
cls1_trip0: cls1-trip-point0 {
temperature = <75000>;
hysteresis = <5000>;
type = "passive";
};
cls1_trip1: cls1-trip-point1 {
temperature = <85000>;
hysteresis = <5000>;
type = "passive";
};
cls1_trip2: cls1-trip-point2 {
temperature = <95000>;
hysteresis = <5000>;
type = "passive";
};
cls1_trip3: cls1-trip-point3 {
temperature = <105000>;
hysteresis = <5000>;
type = "passive";
};
cls1_trip4: cls1-trip-point4 {
temperature = <115000>;
hysteresis = <5000>;
type = "critical";
};
};
};
};
Interface
API
Please refer to the documentation in the kernel directory:
Documentation/driver-api/thermal/
Debugging
sysfs
Please refer to the documentation in the kernel directory:
Documentation/driver-api/thermal/sysfs-api.rst
Testing
Follow the Testing Method section above to validate the thermal driver.